CyanConnode safeguarding Smart meters against cyberattacks
By EPR Magazine Editorial November 21, 2023 11:23 am IST
By EPR Magazine Editorial November 21, 2023 11:23 am IST

Smart meters today are not just about energy consumption recording; they are increasingly interconnected with home management systems, electric vehicles, and renewable energy sources.
Smart meters, being a cornerstone of modern energy infrastructure, are digital devices that meticulously monitor and record electricity, gas, or water consumption, transmitting this data to utilities for both billing and operational purposes. Their role in offering real-time data on energy usage and facilitating more efficient energy management is undeniable. However, their increasing digitization introduces new cyber vulnerabilities.
As the technology evolves, so do the cyber threats. Smart meters today are not just about energy consumption recording; they are increasingly interconnected with home management systems, electric vehicles, and renewable energy sources. This heightened interconnectivity expands the threat landscape, making it crucial to anticipate and mitigate emerging types of cyber-attacks that are more complex and sophisticated.
Threats:
The potential cyber risks linked with smart meters and the broader smart grid are numerous. Attackers can exploit the meters themselves or the supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system that underpins the smart grid. Multiple cyber-attack techniques like phishing, malware attacks, password brute-forcing, denial of service, man-in-the-middle, and SQL injection attacks all stand as potential threats.
Examples from history provide clear evidence of the dangers: the Stuxnet virus in 2007 and the Ukraine power station incident in 2015 being prime instances. Furthermore, the increasing number of cyber incidents in countries like India underscores the rising challenge.
Increasing Interconnectivity and Its Implications:
The rise in interconnectivity in the smart metering ecosystem brings forth a blend of opportunities and vulnerabilities. As smart meters, utility systems, and consumer interfaces become more interconnected, they enable seamless data flow and real-time analytics, greatly enhancing energy management efficiency and user experience. This integration allows for more precise demand forecasting, efficient energy distribution, and the potential integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
Mitigation:
Addressing these concerns, here are pivotal considerations and best practices for fortifying cybersecurity in the smart metering realm:
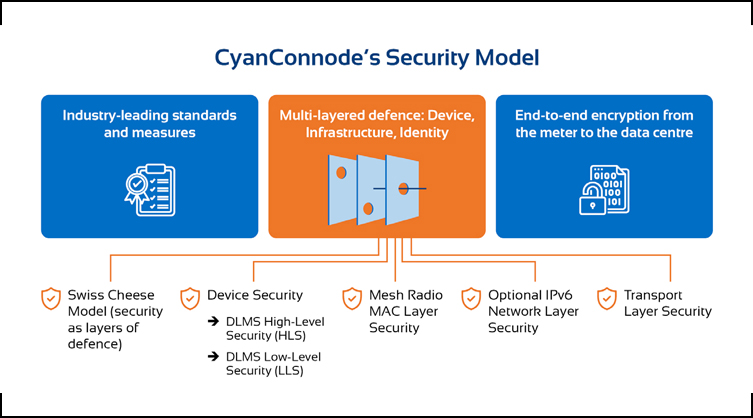
To provide an analogy, the “Swiss Cheese Model” of security can be visualized, where each layer of defence might have holes. These vulnerabilities only pose a risk if an attacker can align and exploit them across multiple layers.
A case in point here is CyanConnode, a leading communications solutions provider for Smart Metering infrastructure in India and globally. The company champions an advanced security model which includes industry-leading standards, end-to-end encryption from the meter to the data centre, and a multi-layered defence strategy spanning across devices, infrastructure, and identity. This robust approach underscores the importance of evolving and adapting to the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity.
Conclusion
The ever-evolving nature of cybersecurity in the smart metering domain demands unwavering vigilance. The entire smart metering ecosystem led by the utilities/ Discoms must synergise to construct and uphold a resilient smart grid infrastructure.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.