Role of RE in the growth of the power sector in India
By EPR Magazine Editorial July 25, 2024 4:04 pm IST
By EPR Magazine Editorial July 25, 2024 4:04 pm IST
This paper examines the role of renewable energy in the growth of the power sector in India, highlighting its importance for energy security, environmental impact reduction, and sustainable economic growth while analysing current developments, policies, challenges, and opportunities in the sector.
Spokespersons: Rajesh Kumar Aroa, Senior Manager, Delhi Transco Limited, and Divyanshu Aroa, Engineering Student
Nowadays, modern society is highly dependent on electrical power supply. To live & make our life comfortable, we use several appliances/gadgets at our residence/office. Every day we get up with the news of electrocution or electrical fires in residential or commercial buildings or public locations or distribution transformers or substations. This forces us to ponder over the reasons/ causes of such accidents which lead to loss of lives as well as assets/properties. This paper provides a root cause analysis of different causes of electrocution or fire hazards for all locations.
Nowadays, modern society is highly dependent on electrical power supply. To live & make our life comfortable, we use a number of appliances/gadgets at our residence/office.
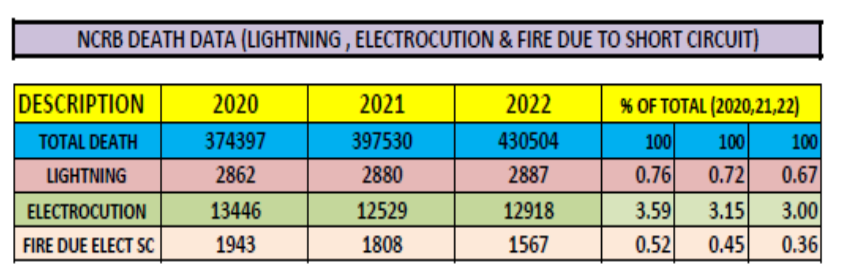
Electrocution, Electrical fire and Lightning kill 15,000 a year. Also, 75000 suffer because of these deaths, there is loss of property and assets, dreams of many people associated with the deceased shatter.
lakh people died due to electrocution in the last decade, as per NCRB data.
NCRB data of deaths due to lightning electrocution and SC fire 2020-222
The news of electric shock or electric fire killing people gives pain and forces everyone to find the solution but, in a day, or two we again forget and wait for another accident to happen.
There are too many tales that different parts of the country have to tell each day without fail (many cases are even not reported or recorded).
Keeping the figure for the injured aside, the numbers for the electrocution deaths in the country tell a story of their own. According to the National Crime Records Bureau, around one lakh people lost their lives because of electrocution in the last decade alone. The annual average of fatalities rose to 12,500 per year or 30 fatalities every day.
Calling the 30 electrocution deaths per day in India “accidents” is something which is not justified as it tends to insulate all stakeholder from accountabilities.
Main causes of electrocution & electrical fire hazard
Electrocution and electrical fires in installations typically stem from several key issues: overcurrents such as overloads and short circuits, harmonics, earth faults, and electric arcs due to loose connections or cable issues. Further risks include the failure or improper selection of protection devices, incorrect cable choices, mismatches in illumination fittings and bulbs, and the use of extension cords for heavy loads like heaters. The use of outdated or damaged equipment, overvoltages from events like lightning, and the transition from consumers to prosumers also contribute to hazards. Additionally, inadequate earthing or grounding designs and insufficient verification and testing of electrical systems can heighten these risks, highlighting the need for diligent electrical design and maintenance.
Role of adequate earthing/grounding
Grounding/ Earthing means making a connection to the general mass of the earth. The use of grounding is so widespread in an electric system that at practically every point in the system, from the generators to the consumers’ equipment, earth connections are made.
There are two types of grounding Neutral Grounding and General Grounding

The objectives of General Grounding system include:
To provide a low resistance return path for fault current which further protects both working staff and equipment installed in the premises (Refer to figure 3).
To prevent dangerous GPR concerning remote ground during fault conditions.
To provide a low resistance path for power system transients such as lightning and overvoltages in the system.
To provide uniform potential bonding /zone of conductive objects within the substation to the grounding system to avoid the development of any dangerous potential between objects (and the earth).
To prevent the building up of electrostatic charge and discharge within the substation, which may result in sparks.
To allow sufficient current to flow safely for satisfactory operation of the protection system.
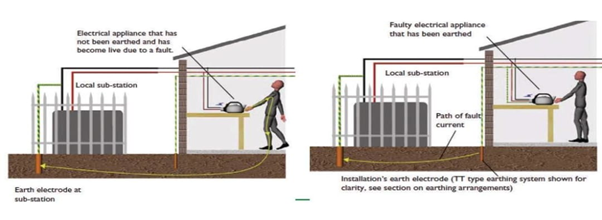
The main objective of grounding electrical systems is to provide a suitably low resistance path for the discharge of fault current which ultimately provides safety to working personnel and costly installed equipment by providing sufficient current to safety devices.
Basic short circuits in the electrical system
Electrical fires very often take place in the residential sector. This is because most people do not account for the rating of the appliances while placing or connecting them. Being an individual, most of us are not aware of the parameters we need to consider while purchasing the product. The only thing that people look for is cost effectiveness which in turn leads to extreme situations resulting in electrical fires. A major reason for an electrical fire in an LV system is short-circuiting i.e. flowing of current through an unintended path.
A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion (please refer Figure 4).
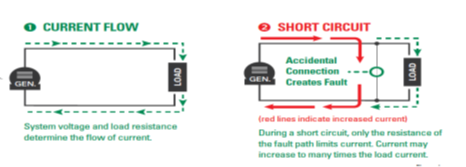
This high current generates high heat and the presence of fuel or any other flammable materials may result in a fire hazard as governed by the fire triangle in Figure 5.
A short circuit happens mainly due to the degradation of insulation. As the wire gets old, the insulation gets degraded, due to which there is a chance of short-circuiting & this may lead to fire.
Main causes of electrocution and electrical fire – different locationsElectrocution and fire hazards pose significant risks to individuals and properties in various settings, including homes, commercial buildings, public places, public processions and substations. These hazards can result in devastating consequences, including loss of life, injuries, and extensive property damage. Understanding the causes behind these incidents is crucial for implementing preventive measures and ensuring safety in these environments. In this section, we will explore the primary causes of electrocution and fire in each of these settings.
Electrical safety at home & commercial shops
Electricity is not something to play around with – neglect and carelessness lead to both electrocution and fire at our homes. Homes are where individuals spend a significant portion of their time, making them susceptible to electrical hazards if proper precautions are not taken. Commercial buildings house various electrical systems to support operations, making them susceptible to electrical hazards if not adequately maintained. Several factors contribute to the risk of electrocution and fire in residential as well as commercial places) are given the table below:
Electrical safety at public places
Public places, such as schools, hospitals, shopping malls, and recreational facilities, accommodate large numbers of people, making electrical safety paramount (refer Figure 7). Electrocution in public places is also evidence of power companies and governments cutting corners. Safety requires discoms to take all high-tension cables underground. But power companies resist this for the costs entailed and direct impact on electricity tariff.
The causes of electrocution and fire in public places are discussed below:
• Aging Infrastructure: Older buildings may have outdated electrical systems, increasing electrical incidents.
• Lack of Maintenance: Inadequate maintenance can lead to deteriorating conditions and hazards.
• Overcrowding: Strain on electrical systems increases the likelihood of overloads and fires.
• Improper Installation: Faulty installation creates hazardous conditions.
• Vandalism or Sabotage: Deliberate acts can result in electrocution hazards and fires.
Electrical safety at public gatherings & processions
Public processions and gatherings hold significant cultural, religious, and social importance in India, often involving large crowds congregating on streets. However, amidst the fervor and celebration, safety concerns often take a backseat, leading to tragic incidents like electrocution & fire.
Causes of Electrocution
Public Events Safety Risks • Improper Wiring: Hasty installations or lack of expertise can lead to faulty wiring setups, increasing the risk of electrocution.
• Overloaded Circuits: Excessive lighting and sound systems during festivals increase electricity demand, increasing the risk of short circuits and electrocution hazards.
• Poor Maintenance: Aging cables, corroded connections, and neglected equipment pose significant threats during large-scale events
. • Unauthorized Installations: Unqualified personnel often install unauthorized installations, bypassing safety protocols and increasing accidents.
• High-Tension Wires: Temporary structures may inadvertently contact high-tension wires during public processions, leading to catastrophic consequences.
Causes of Electrocution Due to High-Tension Wires: Processions Risk Factors
• Inadequate Clearance: Temporary structures often lack proper planning and supervision, increasing the risk of accidental contact with high-tension wires.
• Ignorance and Negligence: Organisers and participants may lack awareness about high-tension wire hazards, leading to increased risk of electrocution incidents.
• Lack of Coordination: Inadequate coordination between event organisers, local authorities, and power distribution companies can lead to haphazard planning and safety measures.
• Encroachment and Unauthorised Construction: Informal settlements and makeshift structures often encroach on safety buffer zones around high-tension wires, increasing the risk of electrocution.
Electrocution from high-tension wires during public events is a preventable tragedy. To address this, India must raise awareness, enforce regulations, conduct pre-event inspections, integrate safety into planning, and enhance emergency preparedness. Proactive measures and collaboration are essential to eliminate this danger from public gatherings, ensuring safety and solidarity during cultural celebrations.
Electrical safety at industrial locations, generating stations & substations
Industries, generating stations, and substations are vital elements of electrical networks, yet they also present significant risks if safety measures are not rigorously upheld. The causes of electrocution and fires in substations include several factors. Firstly, high voltage exposure within these facilities poses a severe risk to untrained individuals or trespassers who inadvertently come into contact with live components. Secondly, equipment failures, such as malfunctions or breakdowns of transformers and circuit breakers, can lead to electrical arcs, sparks, and fires. Thirdly, the lack of proper enclosure exposes electrical components to environmental elements like moisture, debris, and wildlife, heightening the risk of failures and fires. Furthermore, insufficient security measures make substations vulnerable to unauthorised access, potentially resulting in tampering, theft, or vandalism that compromises safety. Lastly, inadequate training for workers in these facilities increases the likelihood of accidents, underscoring the necessity for comprehensive training on electrical safety protocols and emergency procedures to effectively mitigate risks..
Seven Golden Rules to Ensure Safety for Industrial locations and Substation or Generating Station are given below in Table 3.
Seven Golden Rules to ensure safety for Industrial Locations, gen Station & substation
• Evaluate work and conduct an on-site risk assessment.
• identify work location and equipment.
• Apply for a work permit and discuss work details with the team.
• Disconnect electrical sources and secure against reconnection.
• Verify the absence of operating voltages before starting activities.
• Earth is the part where work is to be done.
• Protect adjacent live parts and take precautions near bare conductors.
Electrocution and fire hazards due to contact with overhead power lines or snapping & failure of dt
India’s rapid growth has spurred a surge in electricity demand, prompting extensive expansion of the power network. However, this expansion brings heightened risks of electrocution and fire hazards, particularly from snapped overhead power lines and faulty distribution transformers. In densely populated areas, crisscrossing power lines pose constant dangers, especially to children and pedestrians. Maintenance issues and ageing infrastructure further increase the risk, with rural areas being particularly vulnerable due to delayed repairs. Distribution transformers, vital for electricity supply, are prone to faults like overloading, leading to catastrophic fires. Inadequate cooling systems and degraded insulation materials exacerbate these risks, potentially causing widespread blackouts and economic losses. In urban areas, transformer fires threaten public safety and essential services, overwhelming firefighting efforts and endangering residents and responders.
Electrocution and fire hazards during the rainy season
India faces significant safety challenges during the rainy season and public processions due to heightened risks of electrocution and fire accidents. The period from June to September brings relief from the heat but also poses threats, especially regarding electrical safety. Heavy rainfall and poor infrastructure often lead to electrocution incidents, exacerbated by poorly insulated wires and flooded areas. Waterlogging of streets and residential areas turns them into potential death traps, with damaged power lines adding to the dangers. Illegal tapping of electricity further increases the risk. Electrocution accidents during this time have catastrophic consequences, including loss of life, injuries, property damage, and economic burdens from medical expenses and legal proceedings. Additionally, these accidents can cause power outages, disrupting essential services and inconveniencing the public.
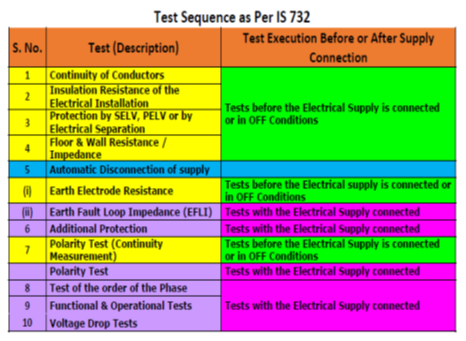
Regular Maintenance & Condition Monitoring testing of all the equipment in the system must be done periodically to avoid any hazards. The list of tests to be conducted is summarised in Table 4 below.
Test to be conducted as per is 732
Regular inspections are crucial for identifying wear, damage, or overloading in electrical systems, wires, outlets, and appliances. Qualified electricians should conduct these inspections. Proper wiring and installation, adherence to building codes, and hiring licensed professionals for installations and repairs are imperative. Overload protection using circuit breakers, fuses, and surge protectors is essential, with even distribution of electrical loads and avoidance of daisy-chaining. Fire safety requires strategic placement and maintenance of smoke alarms, along with appropriate fire extinguishers. Clearance and ventilation around electrical panels, equipment, and outlets prevent overheating. Education on electrical safety practices is vital, as is emergency preparedness and lightning protection. During public events, insulated electrical equipment should be used, cables secured, and water contact avoided. Extra precautions are necessary during rainy seasons or in waterlogged areas. Implementing these measures significantly reduces electrocution and fire hazards.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.