Saving lives and property through passive electrical fire containment
November 22, 2023 6:21 pm
November 22, 2023 6:21 pm
Effective fire safety measures are critical to protect lives and property in India. This comprehensive overview highlights the importance of both active and passive fire protection strategies in mitigating fire risks.
General principle for fire safety (compartmentation)
Effective fire prevention and protection are vital to ensuring the safety of occupants and minimising property damage in India. Government and industry bodies have been working collaboratively to enhance fire safety measures, with a key focus on a combination of active and passive fire protection strategies.
Active fire protection primarily centres on the detection and suppression of fires that are already in progress. Fire detection systems play a crucial role in identifying smoke, flame, and heat. When a fire is detected, the fire alarm panel triggers alarms to alert occupants and initiate evacuation procedures. Simultaneously, it activates the fire suppression system, often employing clean agent gas to extinguish the fire. This synchronised approach ensures the safety of occupants and prevents the escalation of the fire.
However, equally important is fire prevention, which is where passive fire protection measures come into play. Passive fire protection involves strategies to prevent the spread of fire and contain initial outbreaks. Fire-resistant materials, such as coatings applied to electrical cables and fire-resistant walls, floors, and ceilings, are vital in halting the progression of fires. Electrical short-circuits are a common cause of fire accidents, and applying fire-retardant coatings can prevent these incidents from turning into major conflagrations.
Compartmentalisation is another essential aspect of passive fire protection. By dividing a building into separate compartments using fire-resistant barriers, such as fire-resistant walls and floors, the spread of fire can be restricted. This not only prevents fires from spreading but also increases the availability of escape routes for occupants, which is critical for their safety.
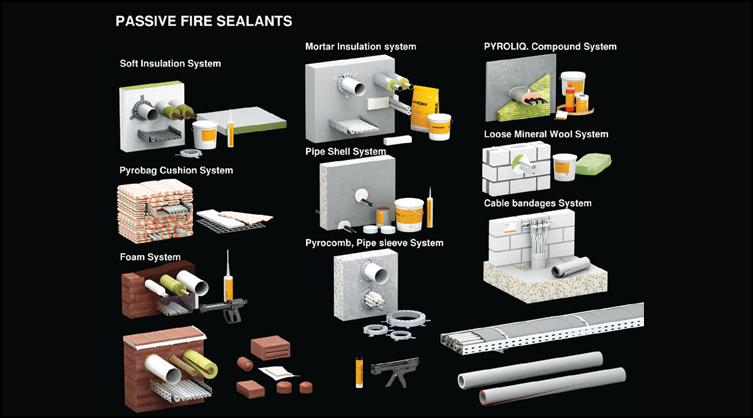
Passive fire sealants are crucial components of fire protection, as they seal openings in walls, floors, and ceilings where electrical conduits, HVAC ducts, and sanitary pipes pass through. When these openings are not adequately sealed, they can allow the fire to breach compartments, resulting in a more significant risk to life and property.
The report on fire accidents in India highlights that 40 percent of the damage is caused by direct fire, while 60 percent is caused by indirect fire factors like heat, smoke, and water. This underscores the importance of both active and passive fire protection. Compliance with fire safety standards is often considered essential, but it is sometimes compromised due to a lack of awareness about passive fire products and the use of sub-standard electrical components.
In cases where data-centric enclosures need safeguarding, a fire suppression system is recommended. However, before installing such a system, a room integrity test should be conducted in accordance with NFPA 2001 guidelines. This test aims to identify any holes or gaps in the room, which, if left unsealed, could lead to the wastage of the clean agent gas. The duration of agent discharge is limited, and if the fire is not contained within this time frame, it can rapidly escalate, causing significant losses.
To address this issue effectively, active and passive fire protection measures need to work in harmony. While active systems detect and suppress fires, passive measures prevent their spread and enhance containment. Together, they create a robust defense against fire accidents, safeguarding lives and property.
Passive fire protection
Passive fire protection is a critical component of building safety and is essential for several reasons. It addresses the limitations and potential failures of active fire suppression systems, making it an integral part of safeguarding human lives and property in the event of a fire.
First and foremost, passive fire protection does not rely on electrical power or complex systems to operate. This means that in the face of power outages, emergency power failures, system malfunctions, or human errors, passive fire protection remains dependable. Even during a fire when active fire suppression systems might fail due to issues like closed valves, insufficient water pressure, external problems, or microorganisms in water lines leading to corrosion, passive fire protection systems continue to function as intended. This resilience is of paramount importance in maintaining a safe environment during a fire emergency.
Passive fire protection includes elements like fire sealants, fire-rated walls, fire-rated doors, and smoke barriers. These components are designed to separate individuals from fire and smoke, preventing their spread and allowing occupants time to evacuate safely. Protected openings in these structures are made with fire-stopping and flame-retardant materials, further containing the fire’s progression.
Furthermore, passive fire protection plays a pivotal role in mitigating the dangers associated with toxic smoke generated during a fire. Toxic smoke, primarily originating from materials like PVC, can pose severe health risks, impairing visibility and causing respiratory distress. In high-rise buildings, where cable insulation is often made from PVC, this risk is particularly pronounced. The adoption of halogen-free installation systems and fire-resistant materials significantly reduces the production of toxic gases, lowering the threat to human life and property.
In locations with critical electrical systems, such as server rooms or UPS rooms, passive fire protection ensures that these systems continue to function during a fire. Fire-resistant chemical products used in openings for electrical cable penetration and plumbing expand when exposed to heat, limiting the transfer of flame, heat, and smoke. This not only protects important electrical systems but also ensures that emergency lighting, smoke evacuation units, and ventilation systems for escape routes remain operational, granting occupants ample time to evacuate and allowing rescue teams to access the building.
National Building Code 2016, Part 4, Annexure C reference
In accordance with the National Building Code (NBC) 2016 Part 4, fire stop compartmentation is defined as spaces within a building enclosed by fire barriers—constructed members with specified fire resistance ratings designed to restrict fire spread and smoke movement. These barriers play a crucial role in maintaining safety. When duct work, plumbing, or electrical systems need to penetrate these barriers, passive fire protection measures must be employed to preserve their integrity.
Clause 4.8 on page 40 of NBC 2016 mandates the installation of a fire-resistant wall with a 120-minute fire rating between transformers. This measure is essential to prevent fire, explosions, or smoke from interfering with safe egress from the building. By strictly adhering to these regulations, buildings can enhance their fire safety and protect occupants in case of emergencies.
National Electrical Code 2023: IEC/IS 61936, reference
The code underscores the imperative need to seal all wiring and pipe passages within building constructions, including floors, walls, roofs, ceilings, and partitions, to prevent the propagation of fire and smoke. This protocol extends to pneumatic and sanitary pipe openings, adhering to prescribed fire-rated sealing standards. The construction sector places a significant emphasis on non-combustible materials and components, designed to facilitate the creation of manageable fire sections based on risk assessment.
Achieving spatial separation and compartmentalisation through structural means proves highly effective in curtailing fire spread within a building and its systems. When structural separation is unfeasible, alternative measures, such as shielded installations with fire-resistant materials and fire protection ducts, or the application of fire-resistant coatings to supports, serve as effective fire mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
A thorough fire protection plan is essential in building and industrial design to prevent fires and safeguard lives and property. Code compliance is vital, and it’s the collective duty of planners, builders, and occupants to ensure it is upheld. Dismissing fires as acts of nature must give way to shared responsibility for reducing fire accidents.
Authored by- Arul Prakash K, Managing Director- OBO Bettermann India Pvt. Ltd.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.